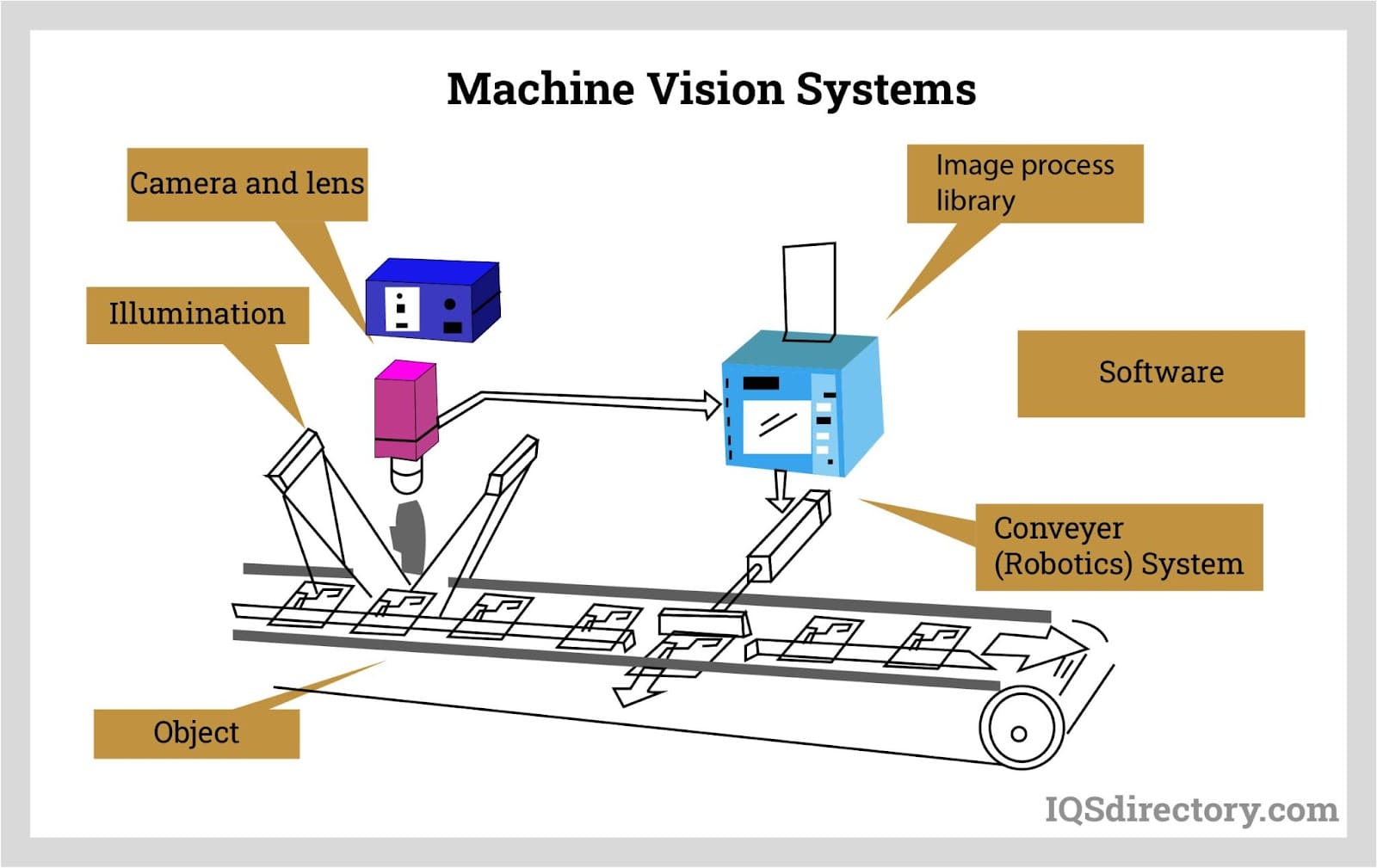
Machine vision systems can be defined as some kind of technology that enables the inspection, evaluation, and identification of still, or moving, images by a computing device. This technology relies on a variety of methods which can be used for different applications ranging from identifying item defects, barcode reading, and product sortation to product checking, end-of-line vehicle inspection, and robotic production. Read More…
When it comes to machine vision systems, we have the tools to get the job done right. We work hard to provide the best solutions and products to meet our customers’ demand. It is our goal to work with you from start to finish on all aspects of design and production. We will do our best to provide the solution to even your most challenging requirements. Find out more by contacting us today!
Our machine vision systems are used around the world in millions of applications. We believe in creating products that work, and our customers trust us to create innovative and effective designs they can rely on. You will find that we face even the most difficult challenges with ease. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you!

At Six Sigma Concepts, LLC, we specialize in designing and integrating advanced machine vision systems that bring precision, consistency, and intelligence to modern manufacturing. We combine engineering expertise with cutting-edge imaging technologies to deliver custom vision solutions that automate inspection, measurement, and process control with remarkable accuracy.

Edmund Optics is a leading optical manufacturer, offering world-class components, assemblies, and services. We can design custom lenses, optical prisms, beamsplitters, optical filters, windows, and laser optics, while offering a range of single/multi-layer coating options.

More Machine Vision System Manufacturers

Types of Machine Vision Systems
Machine vision systems are a core component of modern industrial automation, quality control, and intelligent manufacturing. Choosing the right type of machine vision system is essential for achieving optimal performance in various applications such as inspection, measurement, sorting, and robotic guidance. Below, we outline the primary types of machine vision systems, each designed to meet specific industrial needs and use cases:
1D Vision Systems
1D (one-dimensional) machine vision systems analyze digital signals one line at a time, rather than capturing a full image. These systems excel at detecting and classifying defects in materials produced via continuous processes, such as plastics, paper, metals, textiles, and other non-woven products. By identifying variances in sequentially acquired lines, 1D vision systems help manufacturers achieve superior quality assurance in high-speed environments.
Common 1D vision system applications include:
- Web inspection for paper and plastic film production
- Surface defect detection in metal sheets and wires
- Material thickness and consistency measurement
- Continuous product tracking and monitoring

2D Vision Systems
2D (two-dimensional) vision systems provide area scans, capturing images in an X-Y plane. These systems are the default technology for a wide range of machine vision applications, thanks to their versatility and compatibility with leading vision software platforms. 2D vision systems are ideal for inspecting discrete parts, pattern recognition, barcode reading, and verifying presence or absence of features. They are widely available in a variety of resolutions to match specific application requirements.
Looking for 2D machine vision for quality inspection? 2D vision systems are used in:
- Packaging inspection in food and beverage industries
- Assembly verification in electronics manufacturing
- Label and print quality analysis
- Robotic pick-and-place guidance
3D Vision Systems
3D (three-dimensional) machine vision systems capture depth information to accurately measure and analyze object geometry and spatial relationships. One common 3D approach is stereo vision, which uses two horizontally displaced cameras to reconstruct a 3D image by solving the correspondence problem—matching points between the two images. Other technologies, such as structured light, laser triangulation, and time-of-flight sensors, are also widely used for 3D imaging.
3D vision systems are vital for applications that require precise volume measurement, bin picking, and surface profiling. They enable advanced automation in:
- Automated dimensional measurement
- Complex assembly verification
- Robotic guidance for irregular part handling
- Automated defect detection in automotive and aerospace industries
What Is a Machine Vision System? Exploring the Basics
A machine vision system is an integrated solution comprised of cameras, sensors, lighting, optics, image processing hardware, and specialized software, designed to automatically capture and analyze visual data from the production line or environment. These systems enable machines to "see" and interpret visual information, mimicking and often surpassing human inspection capabilities in speed, accuracy, and consistency.
Want to know how machine vision works and how it can benefit your business? Explore the main components and workflow below:
- Image Acquisition: High-speed industrial cameras or line-scan cameras capture images of products or materials as they pass by on the production line.
- Lighting & Optics: Proper illumination and lens selection are critical to highlight features, enhance contrast, and ensure image clarity.
- Image Processing: Advanced algorithms analyze captured images to identify features, measure dimensions, detect defects, or read codes.
- Decision Making: The system compares analyzed data to predefined criteria, triggering pass/fail decisions, sorting, or automated actions.
- Data Communication: Results and measurement data are shared with factory automation systems, robots, or operators for further action or traceability.
Applications of Machine Vision Systems

Machine vision systems play a transformative role in manufacturing, logistics, and beyond. Their ability to provide real-time, objective, and repeatable analysis makes them indispensable across industries. Below are some of the most valuable applications of machine vision:
- Barcode Reading: Automated reading and verification of 1D and 2D barcodes for product tracking, inventory management, and traceability.
- Defect Detection: Identifying surface flaws, scratches, dents, cracks, or contamination on manufactured parts and finished products.
- Sorting: High-speed sorting of objects based on color, size, shape, or other visual characteristics.
- Vision-Guided Robots: Enhancing robotic arms and pick-and-place systems with precise location and orientation data.
- Traceability: Capturing and recording part or batch information for regulatory compliance and process optimization.
- Pattern Matching: Locating and verifying patterns, logos, or assembly features for quality assurance.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR): Recognition and verification of printed or etched characters for labeling, serial numbers, and expiration dates.
- Color Verification: Ensuring accurate color shades in packaging, automotive components, or consumer electronics.
- Automated Vision Testing and Measurement: Non-contact dimensional measurement, alignment verification, and tolerance checking.
- Presence/Absence Detection: Confirming correct assembly by verifying the presence or absence of parts or features.
- Part Verification: Ensuring the right component is present at each stage of assembly or packaging.
Curious about whether machine vision is right for your operation? Ask these questions:
- What inspection tasks can be automated in your process?
- What types of defects or errors are most costly to your business?
- Could automated measurement improve your quality control?
- Do you need to enhance traceability for regulatory compliance?
- Are you seeking to reduce labor costs or increase production throughput?
Industry Use Cases and Sectors Leveraging Machine Vision
Across many industries, machine vision systems deliver competitive advantages by automating complex visual tasks. Here are some leading sectors and their typical use cases:
- Automotive: Paint finish inspection, weld seam analysis, component verification, and VIN code reading.
- Electronics & Semiconductors: PCB inspection, solder joint analysis, microchip alignment, and defect detection.
- Pharmaceutical & Medical Devices: Label verification, packaging integrity, fill level control, and blister pack inspection for regulatory compliance.
- Food & Beverage: Fill level inspection, seal integrity verification, expiration code reading, and packaging quality control.
- Logistics & Warehousing: Parcel sorting, barcode verification, and automated inventory tracking.
- Textiles & Paper: Surface defect detection, print registration, and consistency monitoring in continuous processes.
- Aerospace: Non-destructive testing, surface flaw detection, and assembly verification for critical components.
- Consumer Goods: Packaging inspection, logo verification, and color consistency analysis.
Benefits of Machine Vision Systems
The implementation of machine vision systems yields a wide array of advantages for manufacturers and logistics providers seeking to optimize their operations. Here are the most significant benefits, each contributing to a compelling return on investment:
Lower Costs
By automating visual inspection and measurement, machine vision systems decrease labor costs and minimize the need for manual quality checks. They reduce scrap rates by catching defects early, lowering material wastage across the production process. Many companies report a substantial drop in operating costs and an increase in overall production efficiency after adopting vision inspection technology.
Elimination of Human Errors
Human inspection is prone to subjectivity, fatigue, and inconsistency—especially over long shifts or high-volume production runs. Machine vision systems provide objective, repeatable, and high-resolution analysis, eliminating human error and ensuring consistent quality standards. With high-resolution cameras, these systems can detect fine details that may be invisible to the human eye, catching subtle defects and improving product reliability.
For example, in electronics manufacturing, machine vision systems inspect thousands of solder joints per minute with greater accuracy than manual inspection. This translates to fewer product recalls, reduced warranty claims, and higher customer satisfaction.
Reduced Downtime
Machine vision inspection is contactless, protecting both products and equipment. By minimizing physical contact, wear and tear on mechanical components is greatly reduced, leading to lower maintenance costs and less unplanned downtime. Automated inspection is faster and more reliable, enabling continuous operation and reducing bottlenecks on the production line.
Wondering how machine vision can boost your uptime? Many manufacturers use real-time inspection data to predict maintenance needs and optimize production scheduling.
Increased Productivity
With automated inspection and measurement, production lines can run at higher speeds without sacrificing quality. Machine vision systems deliver near-instant feedback and corrective commands—often outpacing even trained human operators by several seconds per decision. This accelerates throughput, stabilizes productivity, and helps companies meet tight shipping deadlines or scale up to meet demand surges.
Print Defects Identified
Detecting print anomalies—such as missing letters, incorrect color shades, misalignments, or blemishes—is a common challenge in packaging and labeling. Machine vision systems excel at identifying these issues rapidly and reliably, ensuring that only products meeting brand and regulatory standards reach customers.
Enhanced Safety
Reducing human involvement in dangerous or repetitive tasks enhances workplace safety. Machine vision systems allow operators to monitor processes remotely, lowering the risk of injury from heavy machinery, hazardous materials, or monotonous inspection activities. This not only protects workers but also helps companies comply with workplace safety regulations and reduce insurance costs.
Product Flaw Detection
Advanced vision algorithms can distinguish between acceptable and unacceptable flaws, such as minor surface scratches versus deep dents. By precisely defining defect criteria, manufacturers can improve quality yields, reduce false rejects, and maintain high standards for outgoing products.
More Accurate Measurement
Machine vision systems provide precise, non-contact measurement of critical dimensions such as radius, diameter, depth, and distance. This is essential for industries where tight tolerances and repeatability are required—such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. Vision systems offer superior speed and accuracy compared to manual calipers or gauges, reducing measurement errors and improving process control.
Object Location
Vision-guided robotics depend on machine vision systems to locate and orient objects for automated pick-and-place, assembly, or packaging tasks. By providing real-time coordinates, vision systems enable robots to handle parts accurately, even when their position or orientation varies. This is critical for applications such as random bin picking, flexible assembly, and warehouse automation.
How to Choose the Best Machine Vision System for Your Application
With a vast array of machine vision technologies, selecting the right solution can be complex. Here are some key factors to consider during your evaluation process:
- Type of Inspection: What are your primary inspection or measurement tasks? Do you need defect detection, dimensional measurement, code reading, or color verification?
- Speed and Throughput: What is your required inspection rate? Ensure the vision system can keep pace with your production line without creating bottlenecks.
- Resolution and Accuracy: What level of detail must be detected, and what are your tolerance requirements?
- Lighting and Environmental Conditions: Will the system operate in variable lighting, dusty, or high-vibration environments? Proper lighting and ruggedized equipment may be necessary.
- Integration: Can the vision system interface with your existing PLCs, robots, and MES/ERP systems?
- Scalability: Are you planning to expand or automate additional processes in the future?
- Support and Service: Does the supplier provide technical support, training, and system maintenance?
- Budget and ROI: What is your budget, and how quickly do you expect to see a return on investment?
Need help specifying a machine vision system? Contact multiple suppliers and request application reviews or proof-of-concept demonstrations. Most leading machine vision companies offer feasibility studies and sample testing to optimize solutions to your unique requirements.
Choosing the Right Machine Vision Systems Company
To ensure you achieve the best outcome when purchasing machine vision systems, it is crucial to evaluate multiple suppliers and solution providers. Use our Machine Vision Systems directory to compare at least four qualified vendors. Each supplier’s profile highlights their expertise, system capabilities, and industry experience. You can also contact manufacturers directly for more information or request a customized quote.
Explore each machine vision company’s website using our proprietary website previewer to understand their specialties, technology offerings, and service levels. When ready, use our streamlined RFQ (Request for Quote) form to reach multiple suppliers with a single message, ensuring you receive competitive proposals tailored to your needs.
Questions to Ask When Choosing a Machine Vision Partner
- What experience does the supplier have in your industry or application area?
- Can they provide references or case studies?
- What is their approach to system integration, training, and after-sales support?
- Do they offer on-site installation and commissioning services?
- How quickly can they deliver and support your system?
Frequently Asked Questions About Machine Vision Systems
What is the difference between machine vision and computer vision?
While both terms refer to automated image analysis, machine vision typically describes industrial systems deployed on production lines for real-time inspection, measurement, and guidance. Computer vision is a broader field encompassing research and application in robotics, artificial intelligence, and consumer technology. Machine vision systems are usually optimized for speed, reliability, and integration with factory automation.
How much does a machine vision system cost?
The cost of a machine vision system varies widely based on complexity, camera resolution, processing requirements, integration needs, and support services. Simple vision sensors or smart cameras may start at a few thousand dollars, while complex multi-camera systems can range into six figures. A detailed application review with suppliers is essential for accurate budgeting and ROI estimation.
Can machine vision systems be retrofitted to existing production lines?
Yes. Many manufacturers specialize in retrofitting machine vision solutions to legacy equipment. Factors to consider include available installation space, line speed, and connectivity requirements. An experienced vision integrator can develop customized mounting, lighting, and interface solutions to maximize performance.
What are the latest trends in machine vision technology?
Emerging trends include the use of AI and deep learning for more sophisticated defect detection, 3D vision for complex inspection tasks, embedded smart cameras, and cloud-based analytics for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance. Advances in sensor technology and lighting are also expanding the range of applications for machine vision.
Get Started: Find the Best Machine Vision System for Your Needs
Ready to upgrade your manufacturing quality control, automate inspection, or boost productivity with advanced machine vision? Explore our comprehensive machine vision systems directory to compare leading suppliers, review detailed product offerings, and connect with experts who can design the perfect solution for your operation.
Have more questions? Contact our team of machine vision specialists today for a free consultation or to request a custom quote tailored to your application. Learn how the right machine vision system can transform your business, ensure compliance, and deliver measurable ROI.




 Calibration Services
Calibration Services Clean Rooms
Clean Rooms Data Acquisition Systems
Data Acquisition Systems Dynamometers
Dynamometers Environmental Test Chamber
Environmental Test Chamber Leak Detectors
Leak Detectors Load Cells
Load Cells Machine Vision Systems
Machine Vision Systems Scales
Scales Thermocouples
Thermocouples Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services